Polarizers / Polarizing Prisms
Beam Splitters

Beam Splitters are optical components that divide light into transmitted and reflected beams.Depending on the purpose, half mirrors with metallic coatings or polarizing films with dielectric coatings are selected.
- Fiber Optics (FTTH)
- Medical Equipment
- Aviation/Aerospace
- Survey Equipment
- Measuring Instruments
- Optical Sensors
Polarizing Beam Splitters

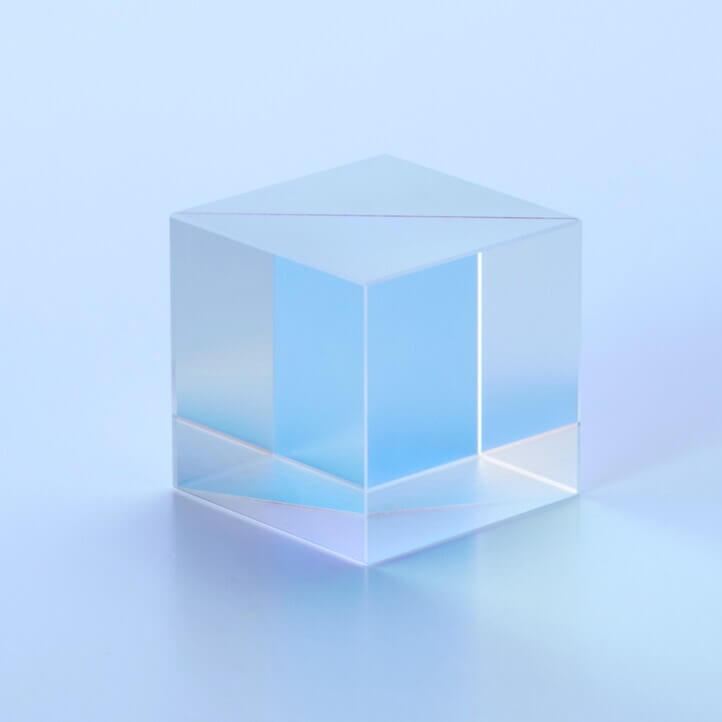
: Polarization Beam Splitter : PBS
Polarizing Beam Splitter (PBS) is an optical element (polarizer) that divides an incident beam into P and S polarizations.
- Semiconductors/LCD Lithography Equipment
- Laser Interferometers
- Survey Equipment
- Measuring Instruments
- Satellite
- Bioanalysis
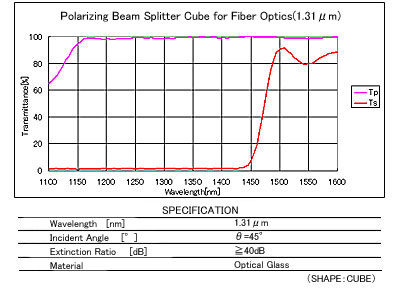
Polarizing Beam Splitter Cube for Fiber Optics(1.31μm)
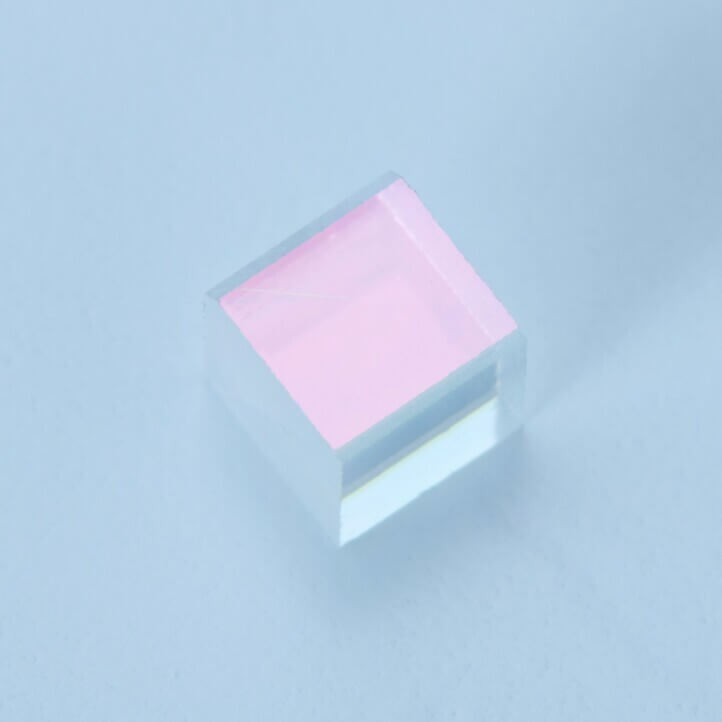

: Polarizing Beam Splitter Cube for Optical Communications(1.31μm)
Polarizing Beam Splitters for Fiber Optics provide isolation with the P-/S-polarization extinction ratio of 1/10,000 or more.
- Fiber Optics for Isolators
- Fiber Amplifiers
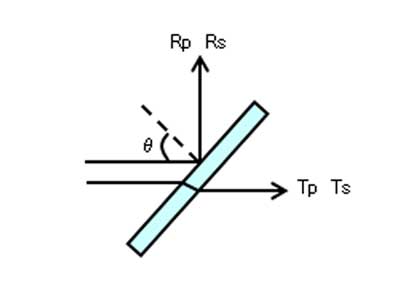
Beam Path
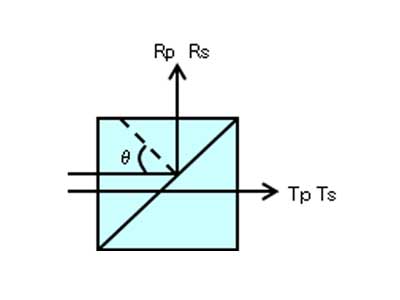
Spectral Characteristics / Specifications
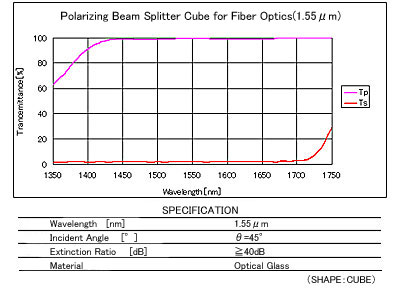
Polarizing Beam Splitter Cube for Fiber Optics(1.55μm)
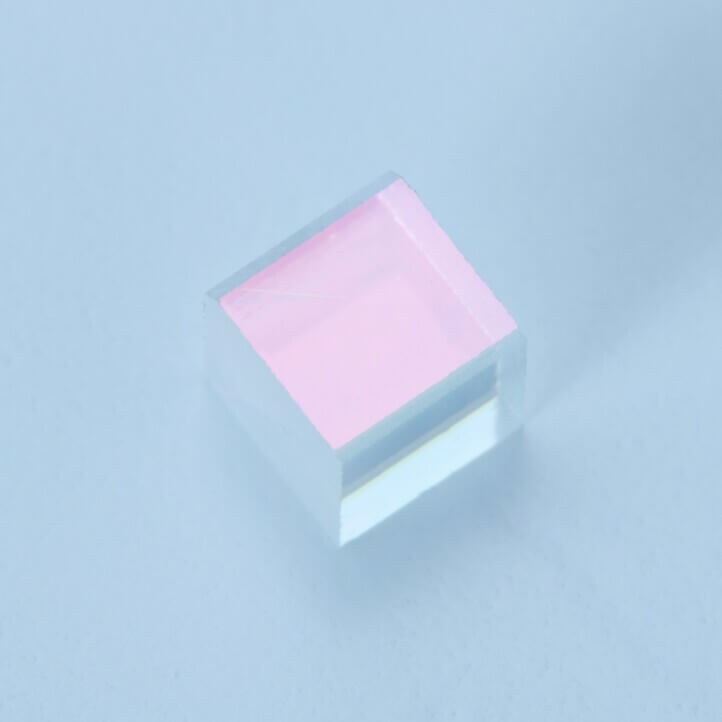

: Polarizing Beam Splitter Cube for Optical Communications(1.55μm)
Polarizing Beam Splitters for Fiber Optics provide isolation with the P-/S-polarization extinction ratio of 1/10,000 or more.
- Fiber Optics for Isolators
- Fiber Amplifiers
Beam Path
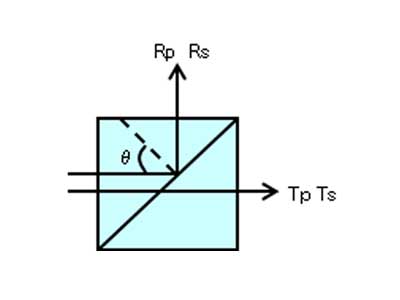
Spectral Characteristics / Specifications
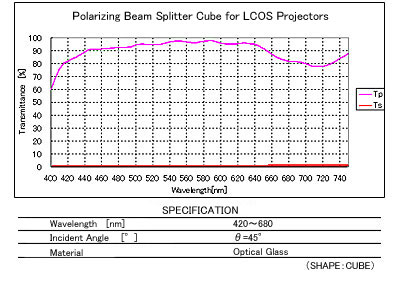
Polarizing Beam Splitter Cube for LCOS Projectors
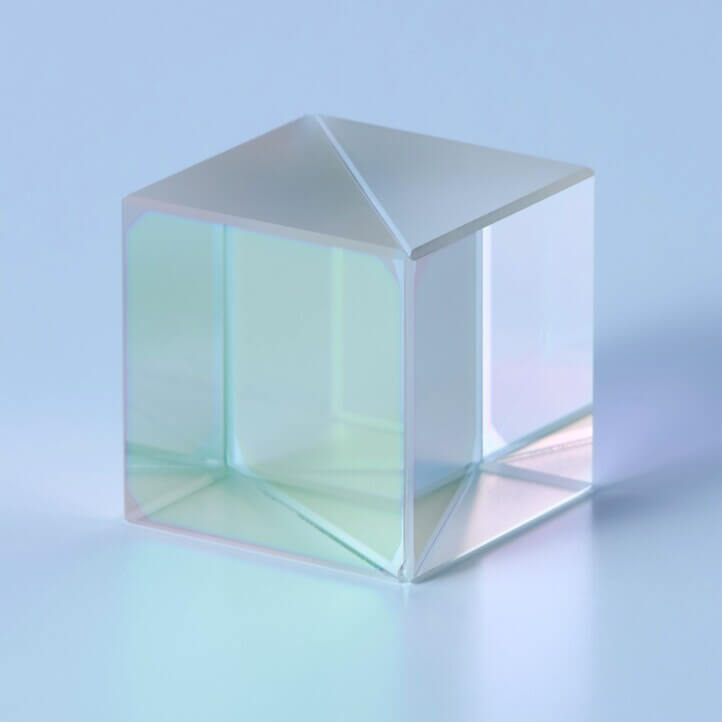

: VIS-Polarizing Beam Splitter Cube
This Polarizing Beam Splitter is used especially for high precision LCOS projectors.This beam splitter is made of low photoelastic coefficient glass to avoid heat influence and has low dependency on incident angle.
- LCOS Projectors
Beam Path
Spectral Characteristics / Specifications
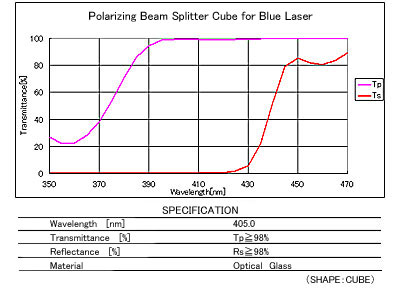
Polarizing Beam Splitter Cube for Blue Laser
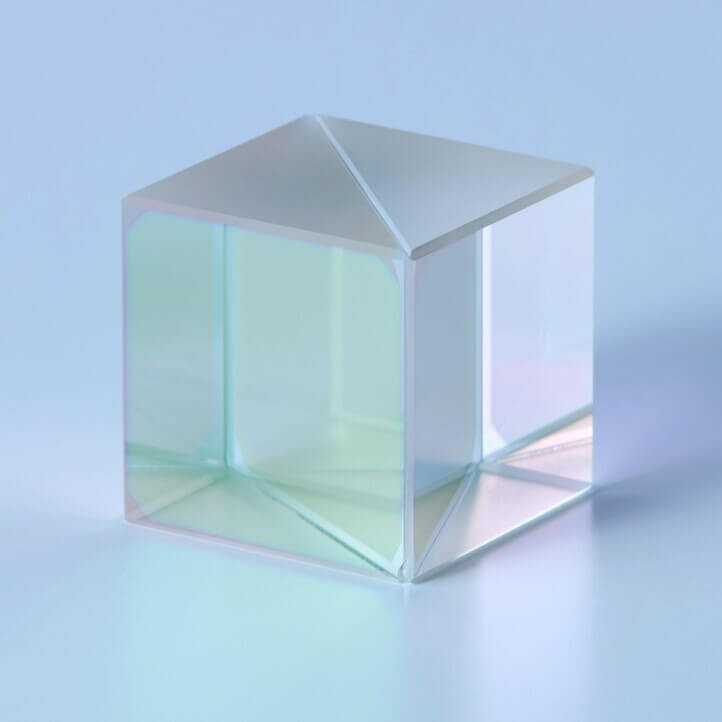

This Polarizing Beam Splitter Cube was developed specially for Blu-ray Disc, HD DVD applications.
- Measuring Instruments
- Inspection Equipment
Beam Path
Spectral Characteristics / Specifications
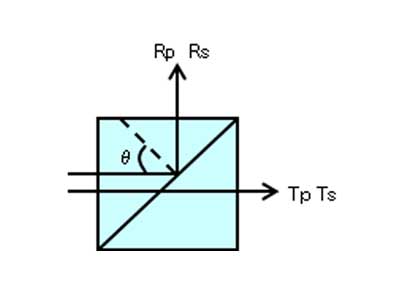
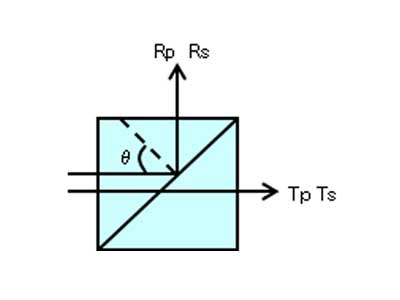
Polarizing Beam Splitter Cube for Measurement/Inspection Instruments
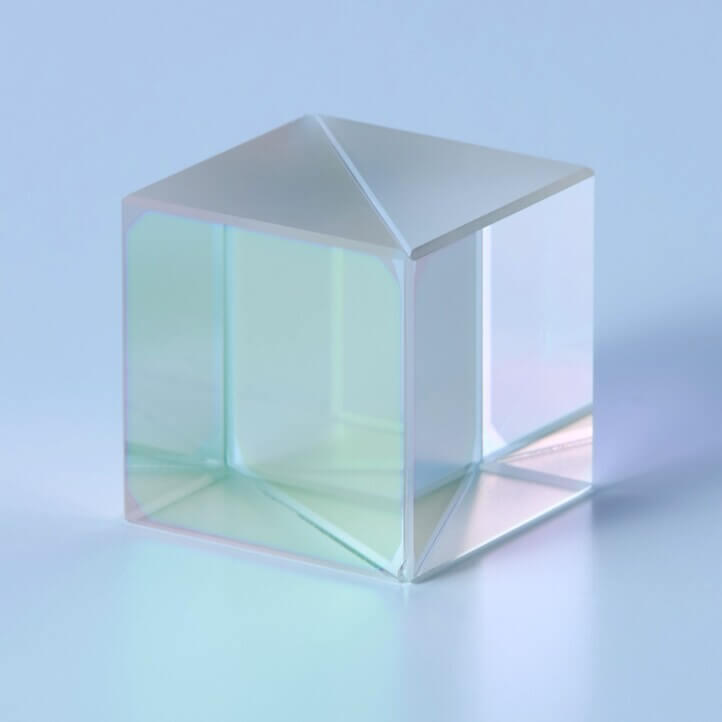

Polarizing Beam Splitter divides P- and S-polarizations to control the direction and intensity of light, enabling precise measurement and inspection.
With dielectric multilayer coatings, it achieves a high extinction ratio and stable spectral characteristics, and is widely used in high-precision optical systems such as interferometers and inspection instruments.
- Measuring / Inspection Instruments
Beam Path
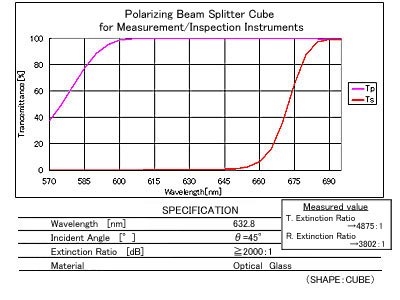
Spectral Characteristics / Specifications
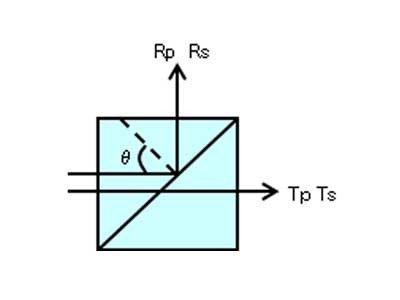
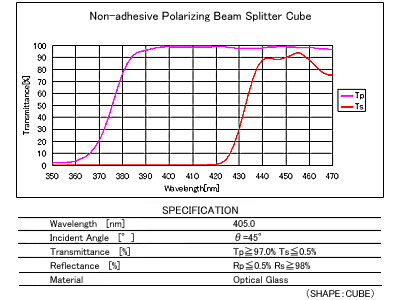
Non-adhesive Polarizing Beam Splitter Cube
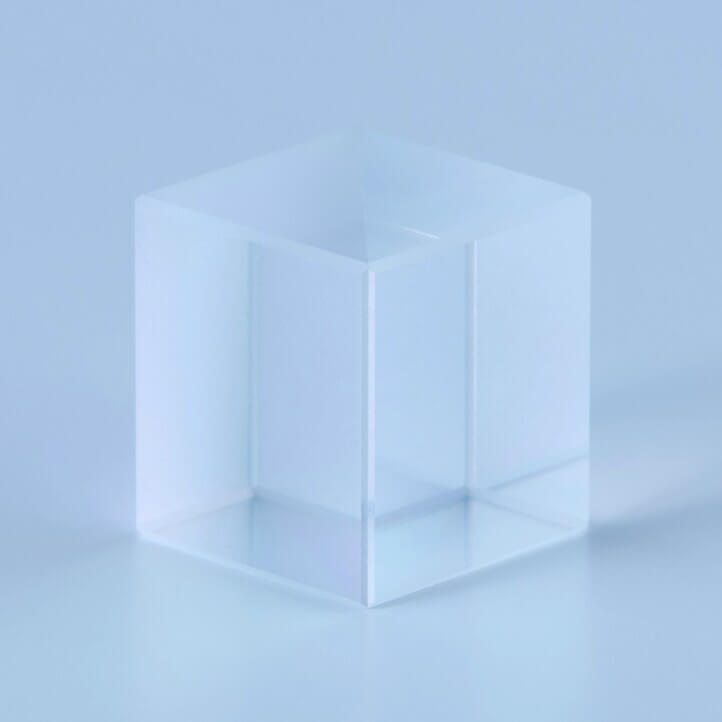

Non-adhesive Polarizing Beam Splitter adopts a bonding method without adhesives to prevent degradation caused by heat and light, ensuring the required optical properties and long-term reliability of the equipment.
- Aviation/Aerospace
Beam Path
Spectral Characteristics / Specifications
Non-polarizing Beam Splitters
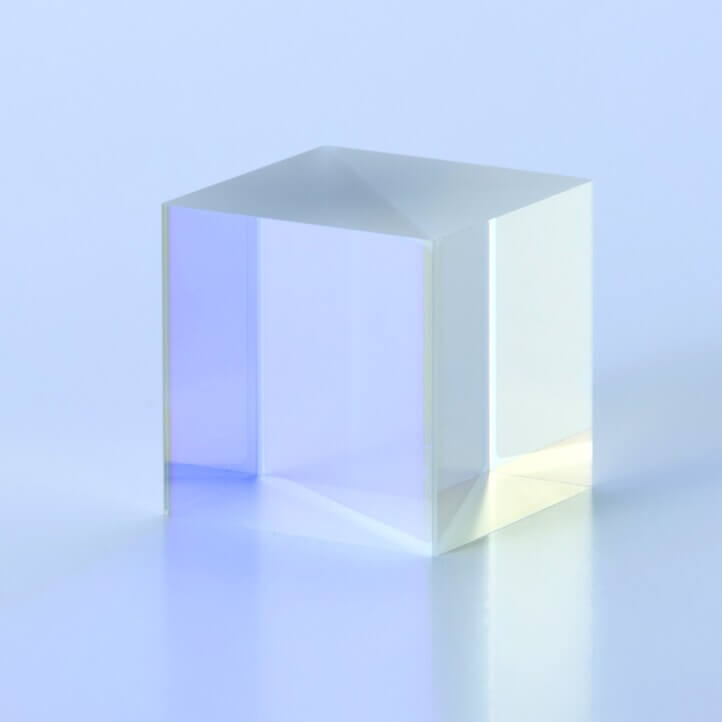

: NPBS
Non-polarizing Beam Splitters (NPBS) equally transmit and reflect P- and S-polarizations.
They maintain the polarization ratio of the incident light when dividing into transmitted and reflected beams.
- Semiconductors/LCD Lithography Equipment
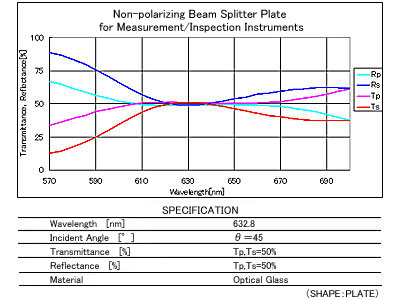
Non-polarizing Beam Splitter Plate
Non-polarizing Beam Splitter Plate is an optical component that distributes transmitted and reflected light equally, independent of the polarization state of the incident light.
- Inspection Equipment
- Measuring Instruments
Beam Path
Spectral Characteristics / Specifications
Non-polarizing Beam Splitter Cube
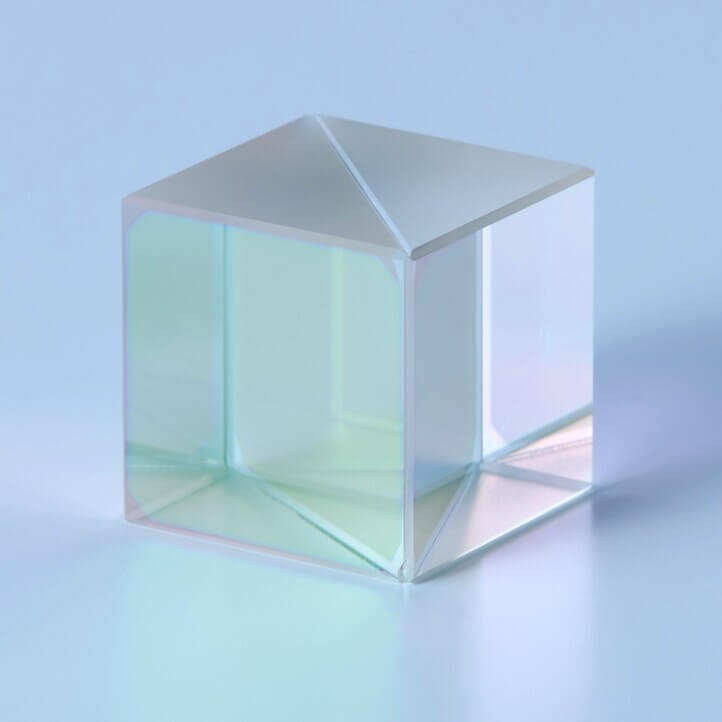

Non-polarizing Beam Splitter Cube is an optical component that distributes transmitted and reflected light equally, independent of the polarization state of the incident light.
- Inspection Equipment
- Measuring Instruments
Beam Path
Spectral Characteristics / Specifications
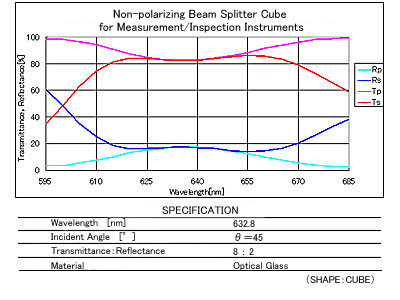
Polarizing Converters
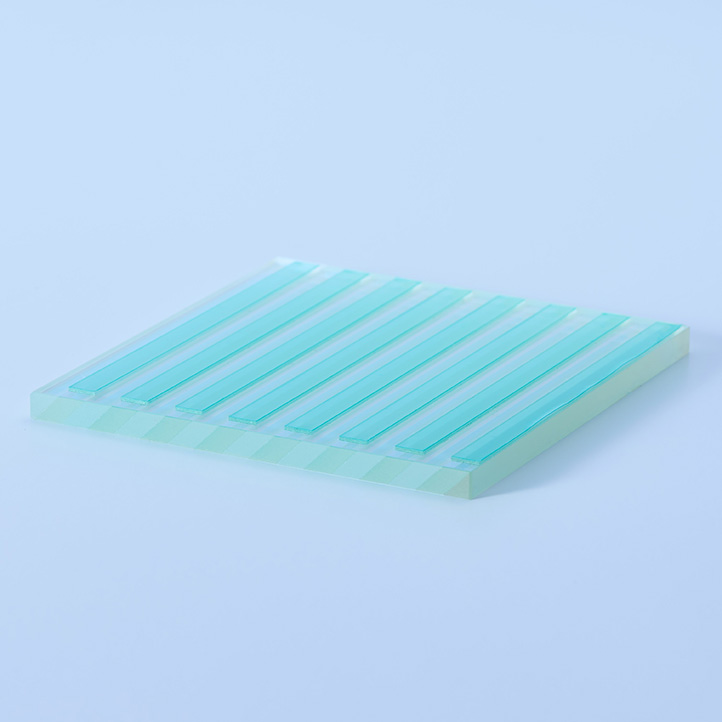

: PLC
Polarizing Converter for LCD projectors divides the incoming random light into P or S polarization in order to increase light efficiency. Either the P or S polarization light passes through 1/2 wave plate and the light is unified to one polarization.
- LCD/LCOS Projectors
Beam Path
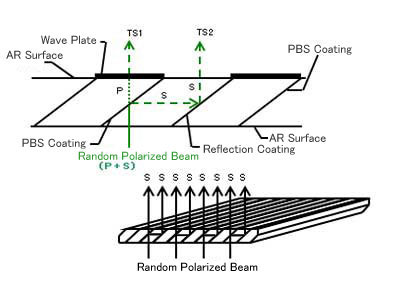
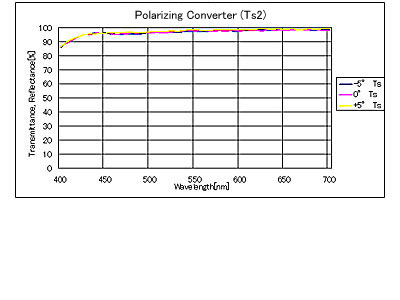
Spectral Characteristics / Specifications1
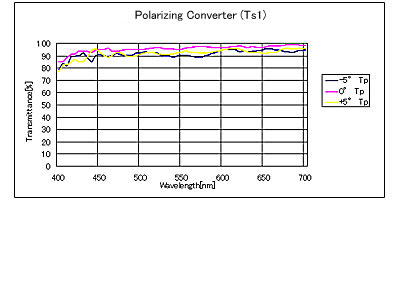
Spectral Characteristics / Specifications2
Wave Plates

Wave Plates are optical components used to control polarization.
Typical examples include half-wave plates (λ/2) and quarter-wave plates (λ/4).
- Fiber Optics
- Semiconductors/LCD Lithography Equipment
- LCD/LCOS Projectors
- Measuring Instruments
- Bioanalysis
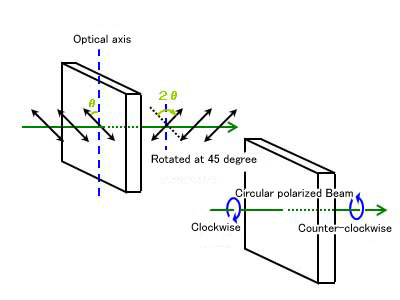
Half-wave Plate

: λ/2 Wave Plates : 1/2 Wave Plates
Wave plates change the polarization optical path difference that oscillates in a perpendicular direction by 1/2 wavelength.
- Fiber Optics
- Semiconductors/LCD Lithography Equipment
- LCD/LCOS Projectors
- Measuring Instruments
- Bioanalysis
Beam Path
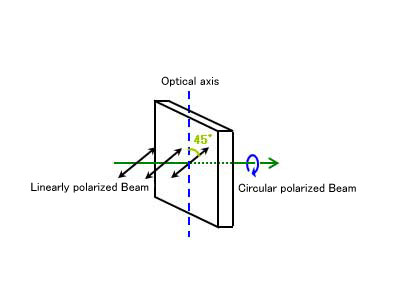
Quarter-wave Plate

: λ/4 Wave Plates : 1/4 Wave Plates
Wave plates change the polarization optical path difference that oscillates in a perpendicular direction by 1/4 wavelength.
- Fiber Optics
- Semiconductors/LCD Lithography Equipment
- LCD/LCOS Projectors
- Measuring Instruments
- Bioanalysis
Beam Path
Optical Contact Type (Wave Plate)
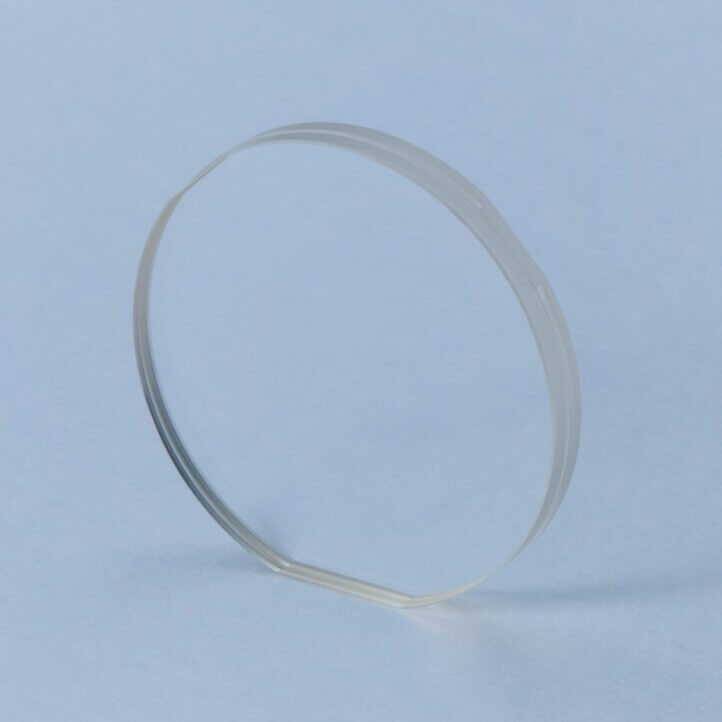

: Non-adhesive Wave Plate
Optical Contact Type Wave Plates are compound zero-order wave plates joined without adhesives.
They can be used with high-power lasers. Since there is no UV absorption by adhesive layers, it provides high transmission in the ultraviolet range and ensures long-term reliability.
- Semiconductors/LCD Lithography Equipment
Beam Path
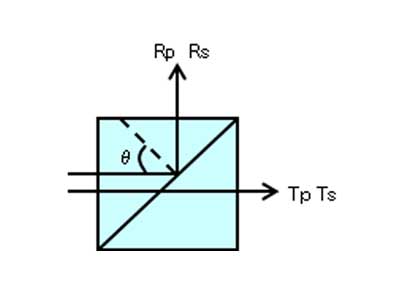
Optical Contact Type (PBS Cube)
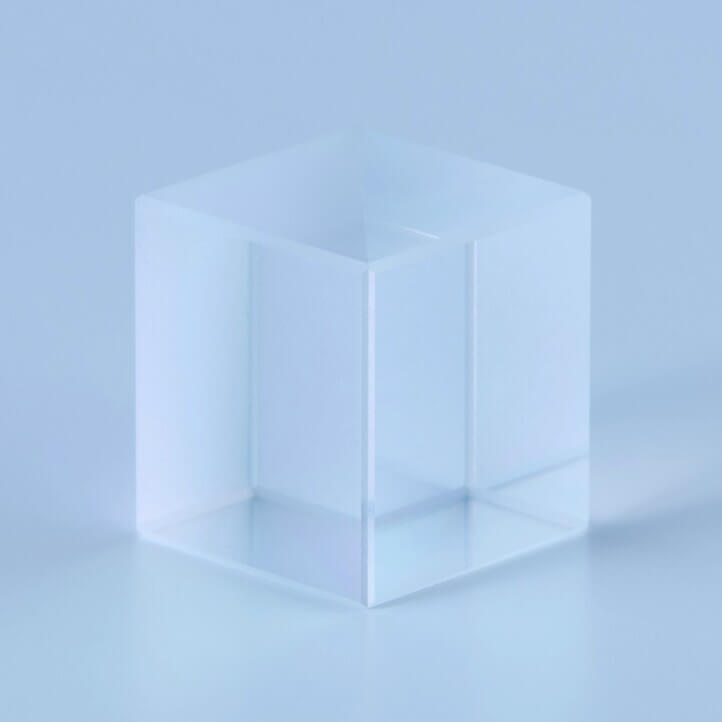

: Non-adhesive Polarizing Beam Splitter Cube
Optical Contact Type polarizing beam splitter (PBS) is a PBS prism joined without adhesives.
It prevents transmission loss even under high-power laser irradiation.
Since there is no UV absorption by adhesive layers, it provides high transmission in the ultraviolet range and ensures long-term reliability.
- Semiconductors/LCD Lithography Equipment
- Optical components for high power laser
Beam Path
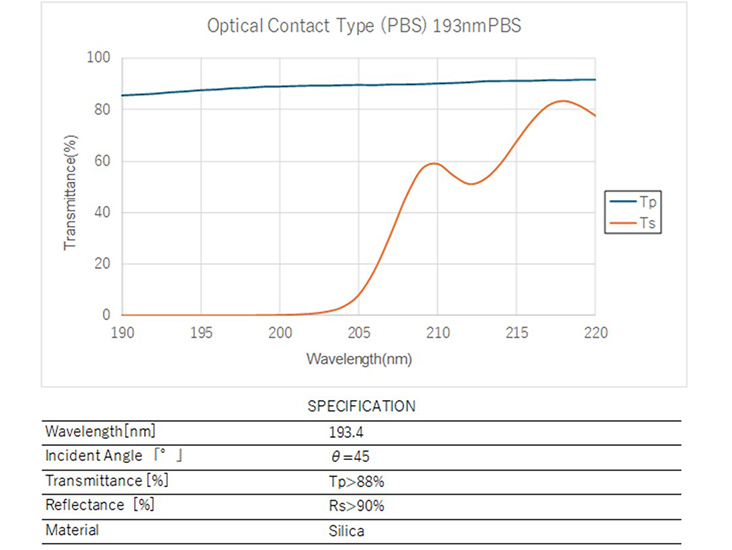
Spectral Characteristics / Specifications1
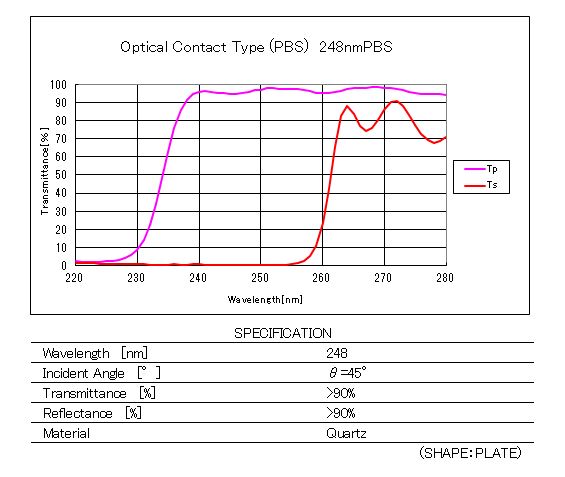
Spectral Characteristics / Specifications2
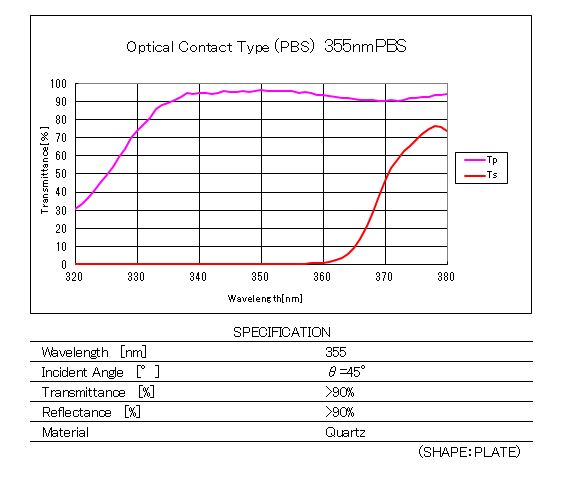
Spectral Characteristics / Specifications 3
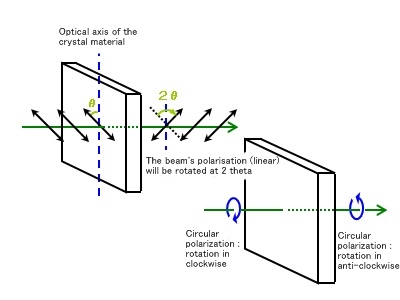
Wollaston Prisms
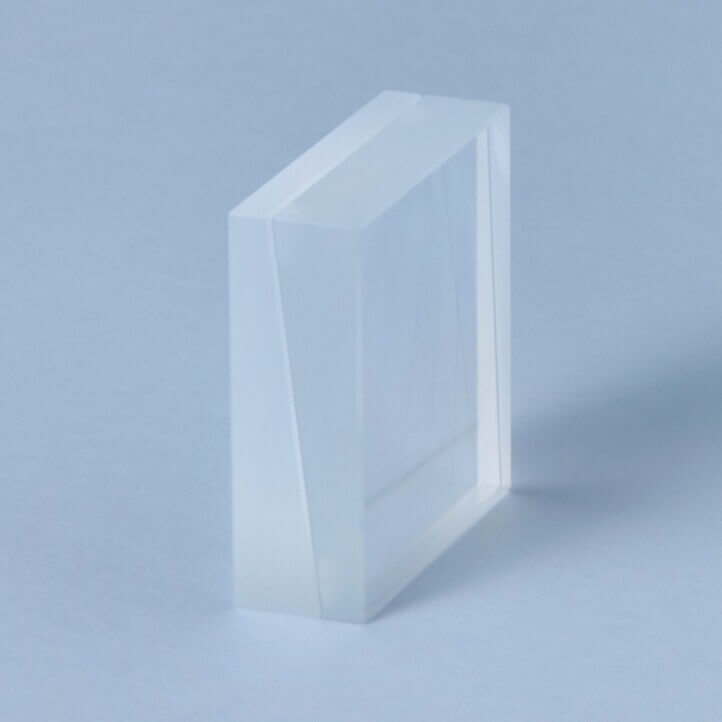

Wollaston Prisms are polarizing prisms composed of two cemented prisms of quartz and calcite.
Light incident entered perpendicularly is refracted inside the prisms and divided into P- and S-polarized beams at the output.
- Analysis Equipment
- Polarizers
Beam Path
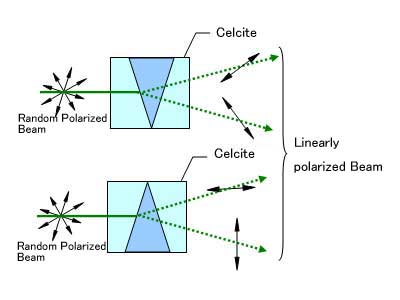
Double Wollaston Prism
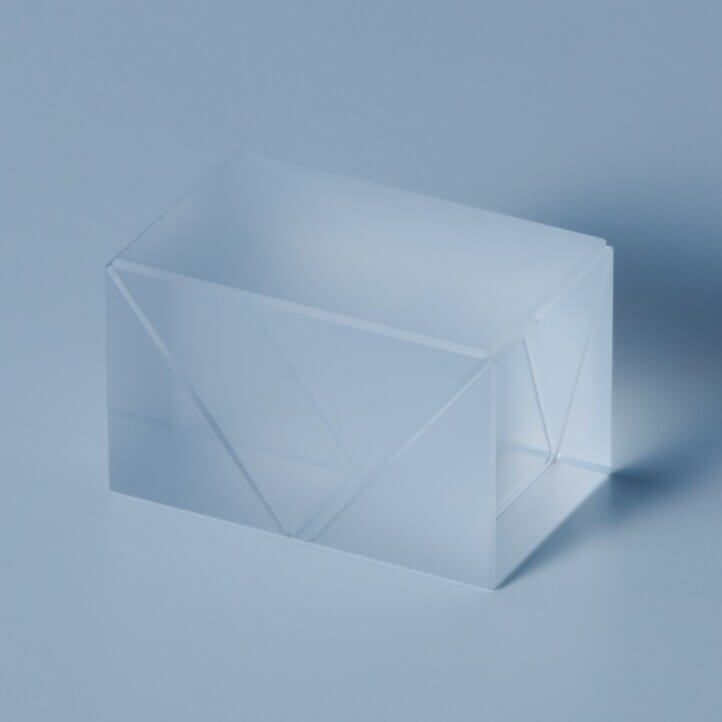

Double Wollaston Prism generates four light beams with polarization axes differing by 45 degrees.
When used as an analyzer in polarization analysis optical systems, it enables acquisition of Stokes parameters in a single exposure without using retardation plates.
Nitto Optical realizes this element with calcite, a soft crystal. (Reference size: 40 × 40 × 30t)
- Aviation/Aerospace
- Analysis Equipment
- Polarizers
Beam Path
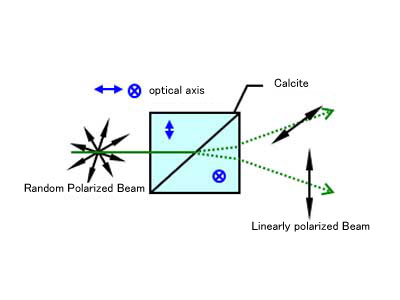
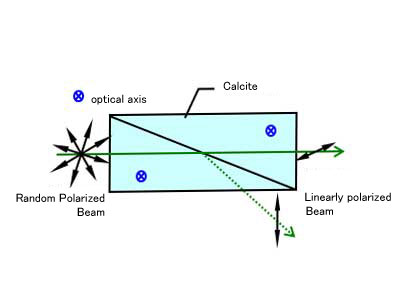
Nicol Prisms

Nicol Prisms are polarizing prisms composed of two calcite crystals with birefringence, joined together to convert incident natural light into linearly polarized light.
- Analysis Equipment
- Polarizers
Beam Path
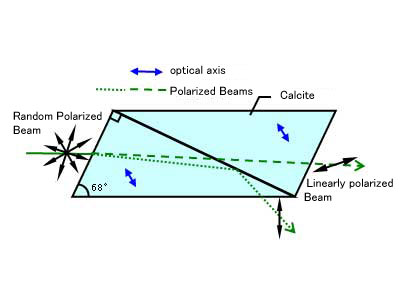
Rochon Prisms

Rochon Prisms are polarizing prisms composed of two cemented right-angle prisms of quartz and calcite.
Light incident entered perpendicularly is divided into two orthogonal emergent beams, with P-polarization transmitted straight and S-polarization deviated at an angle.
- Analysis Equipment
- Polarizers
Beam Path
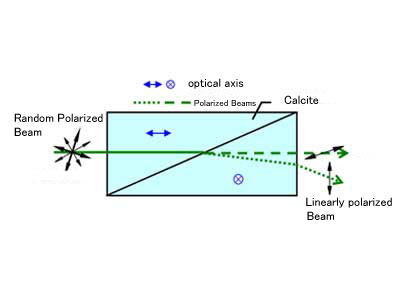
Glan-Thompson Prisms

Glan-Thompson Prisms are polarizing prisms that convert incident natural light into linearly polarized light.
- Analysis Equipment
- Polarizers
Beam Path
 Contact
Contact Search by Product Category
Search by Product Category Search by Industries and Applications
Search by Industries and Applications